VERTICAL FARMING IS THE FUTURE
As has been widely reported, our planet's population is growing faster than we can feed it. Over the next 30 years, we will need to feed 10 billion people with less water and less productive land, all while the climate is rapidly changing. Producing safe food with fewer resources will necessitate more inventive and dependable methods in order to feed the world.
What is vertical farming?
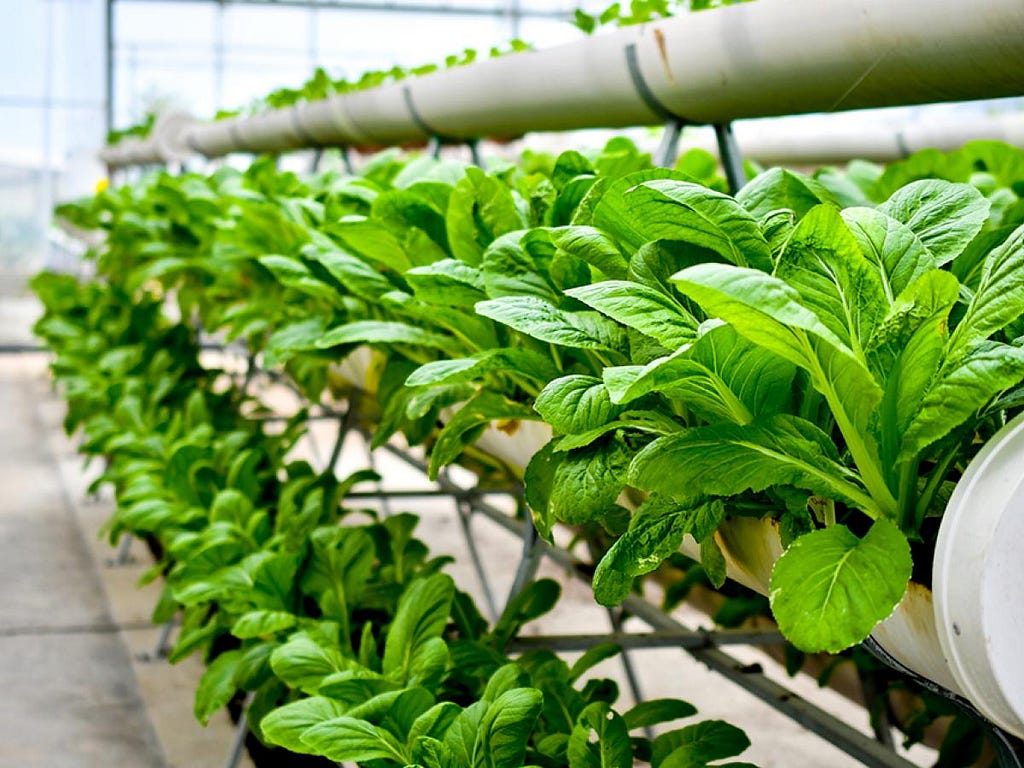
Vertical farming involves layering crops on top of one another rather than growing them in traditional horizontal rows. Because vertical growth conserves space, it increases crop output per square foot of land used. Vertical farms are typically found indoors, such as in a warehouse, where environmental factors that aid plant growth can be controlled.
The Babylonians invented the most well-known example of early advanced agricultural systems. Their hanging gardens, which were built nearly 2,500 years ago, are thought to be the first prototype of a vertical farm. Even if they did not understand the underlying science, ancient people understood that hydroponic plants could be grown without soil.
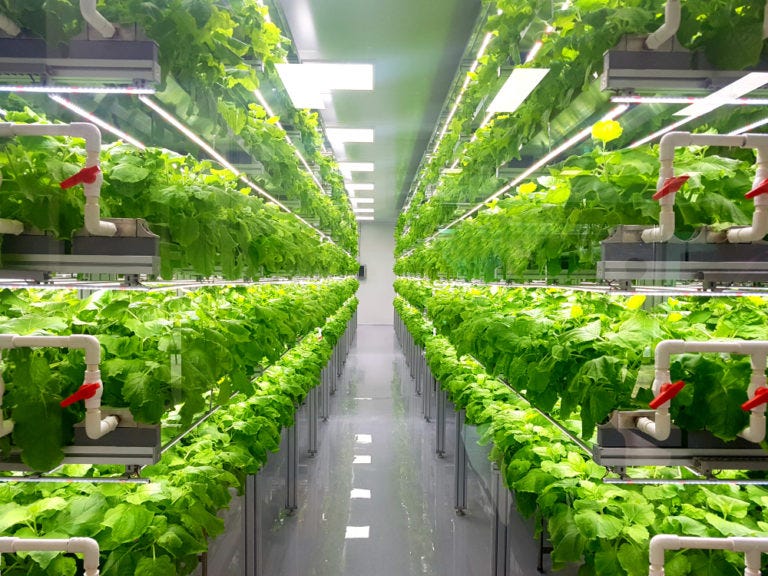

How does vertical farming work?
Yes, it appears that vertical farming may be the answer to many of agriculture's problems, providing us with more food on less land while remaining sustainable. But how exactly does vertical farming work? There are several models available, ranging from patio gardens constructed out of old pallets to warehouses and greenhouses that produce food for entire communities. Here's a breakdown of how vertical farming greenhouses work.
Vertical farming techniques do not require the use of soil. It is possible to grow a healthy plant without the use of hazardous chemicals. Farmers typically use expanded clay, hemp, and coconut fibers, as well as mineral wool. Crops are protected from outside elements and dangers by specialized, hygienic air vents in indoor vertical garden systems. Furthermore, sustainable practices can reduce water consumption by up to 95%.
Vertical farms are increasingly being used by businesses to implement renewable technologies. It reduces the carbon footprint of the solution while increasing its energy efficiency and allowing for a faster return on investment.
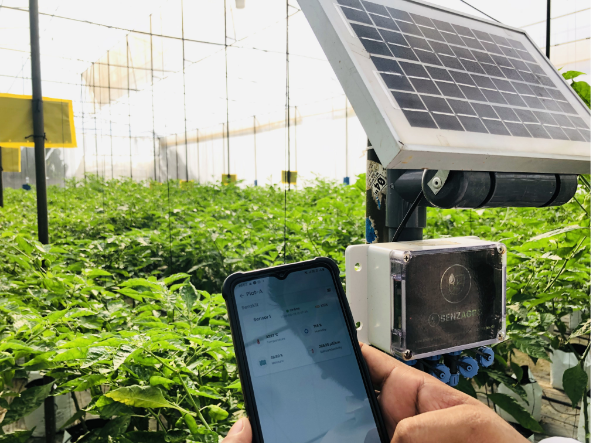
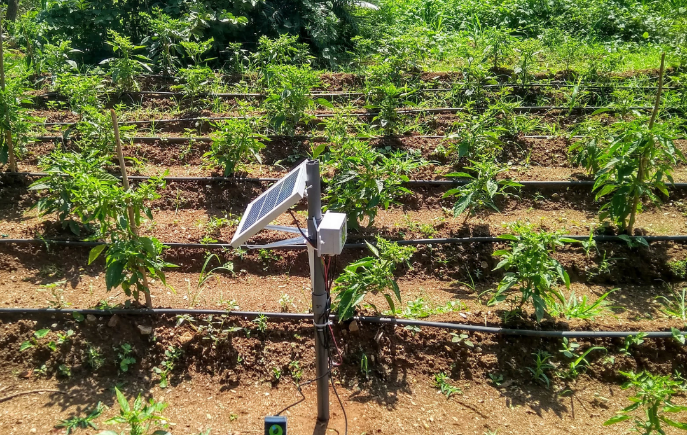
SenzAgro, a global real-time agricultural ecosystem intelligence platform, automates the entire process to provide precise watering, temperature, lighting, and nutrients in order to create the ideal environment. Vertical gardens, live walls, and roof-top gardens require precise environmental conditions in order for plants to grow and produce a higher yield. SenzAgro successfully operates with vertically grown plants and increases productivity by utilizing a low-cost automated system.

Advantages and disadvantages of vertical farming technology
Advantages
- Assurance of Consistent Crop Production
- Optimum land utilization
- Environmental Benefits
- Water Conservation: One of the primary benefits of vertical farming is that it employs a hydroponic growing method that requires only 10% of the water that conventional farming does. Furthermore, this type of farming uses less fertilizer and nutrients than traditional farming methods. This is achieved by growing plants in soil-free and pesticide-free environments under artificial lights. Water evaporated from the plants is captured and reused.
- Reduced carbon emissions: By producing more fruits and vegetables, the need to import from other countries is eliminated.Crop producers can change nutrient management practices to reduce emissions from nitrogen fertilizers and manure applied to farmers’ fields
- Energy generation: Methane produced by composting plant remains has the potential to be used to generate energy.
- No chemicals or pesticides used
- Increased Profits
One of the primary benefits of vertical farming is its dependability. This means that if you choose vertical farming, your crop output will be consistent throughout the year. This is further facilitated by the fact that vertical farming is typically not weather dependent, allowing you to plant crops without fear of bad weather.
For conventional farming, large areas of completely fertile soil are required. Vertical farming, on the other hand, has no such requirements. You can produce more on a small plot of land.
The following are the primary environmental benefits of vertical farming:
Because the moisture level is now properly controlled, crop damage and a variety of fungal illnesses are no longer a possibility. Finally, you have a superior product that is also safer and healthier to consume. Vertical farming is environmentally friendly.
Farmers find it easier to increase their revenues as the processes become more scientific. Optimal cultivation methods yield a larger crop, which means more goods to sell and more money. Furthermore, because vertically grown plants are organic and healthier than horizontally grown plants, producers may be able to use this to justify higher unit costs.
Disadvantages
- High start-upcosts
- High power consumption
- pollination Difficulties
- Only a few crops are profitable to cultivate.
The initial investment is high due to the complexity of developing a commercial plant. As a result, you must exercise caution when making decisions regarding the development of your farm. Once you've decided on a concept, it can be difficult to change your mind once the facility is built, which could result in an unexpected financial burden.
Indoor vertical garden systems require artificial lighting 24 hours a day, seven days a week. As a result, even with LED lighting, the electricity cost will be very high.
At best, the closed system of a vertical farm ensures that no pests enter while also ensuring that no insects exist. This results in pollination, which is a serious problem. In nature, a wide variety of insects transport pollen-laden flights from flower to flower. However, because these insects are not present in vertical farms, manual pollination is required to ensure a successful harvest.
Unfortunately, only a few plants can currently be grown successfully in a vertical farm. This is due to the high cost of growing a plant. Potatoes, despite their low cost, are simply not worth it. As a result, it is currently best to select plants with high economic potential.
How much food can a vertical farm produce compared to traditional farming?
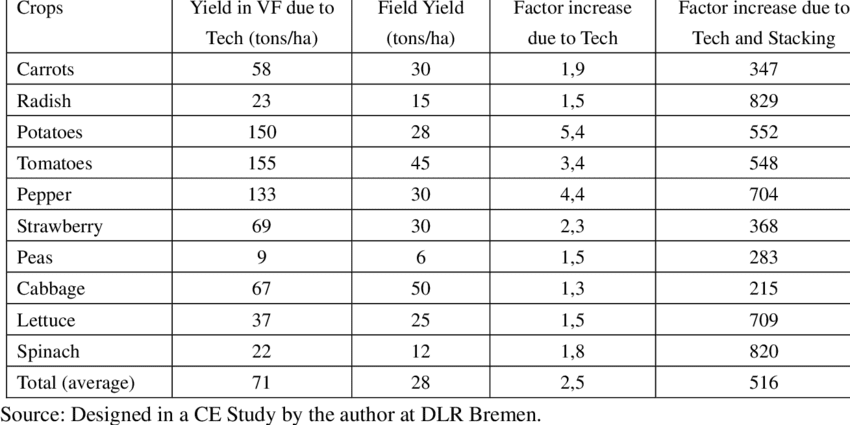
According to the above statistics, research conducted by the Journal of ResearchGate concluded that vertical farms produce an average of 71 times the amount of harvest as traditional field farms. (I obtained this figure from the table above.)
Vertical farming uses much less water and land than traditional farming, emits less CO2, and produces higher crop yields overall and per square foot.
leading country for vertical farming.
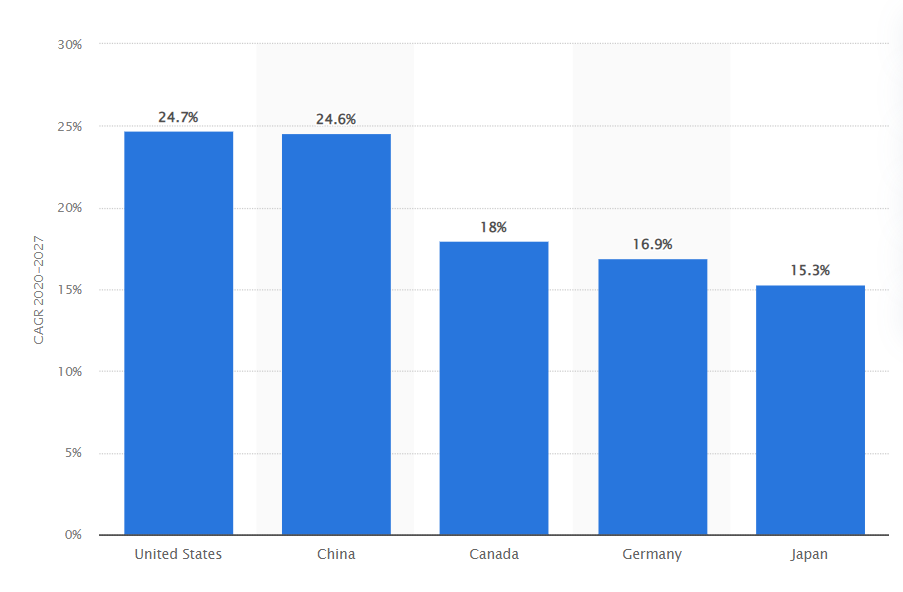
Currently, the country with the highest number of vertical farms is the USA .
Vertical hydroponic farms are now commonplace throughout the Philippines. Vertical farming has grown in popularity in the Philippines because previously imported products can now be grown in built-up urban areas using cutting-edge technology suitable for the country's harsh climate and supplying Filipinos with large yields of fresh organic produce.
3 Types of vertical farming
1.Hydroponics
Hydroponics is the most commonly used growing method in vertical farms. Plants are grown in nutrient solutions rather than dirt in this technique.
In order for plant roots to grow, the nutrient solution in a grow tray must be deep enough to submerge the roots. A reservoir beneath the grow tray, a water pump, and a timer are used to fill the grow tray with nutrient solution several times throughout the day. The timer is set based on factors such as plant size, water and food requirements, development cycles, and ambient temperature.
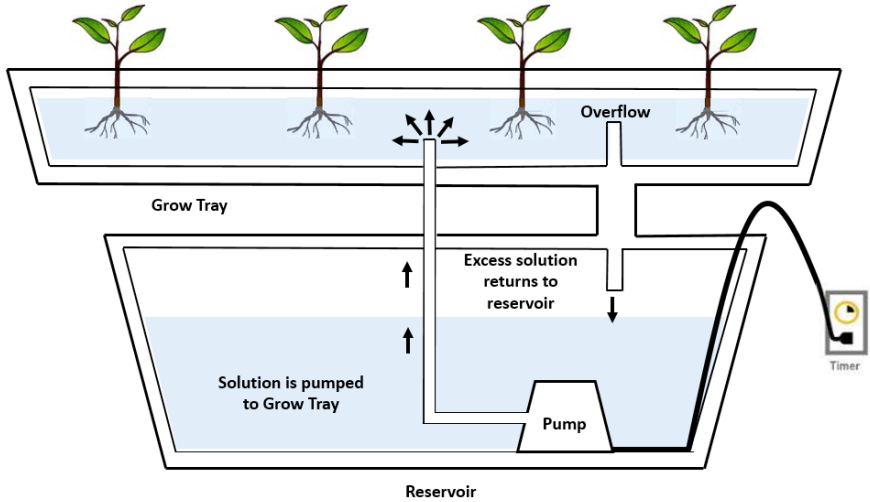
2.Aeroponic
Plants are grown in an aeroponic system without soil and with only a very small amount of water or mist. In this system, the plant roots are suspended in the air. As a result, the root zones are continuously misted with a nutritious solution using a tiny sprayer to ensure that the roots receive enough oxygen. Plants grow faster in this system than in other types of hydroponic systems, making it the most effective vertical farming system.
Furthermore, it consumes 90% less water than the most efficient hydroponic systems. Furthermore, crop yields increase by 45 to 75% while fertilizer use decreases by 60%.
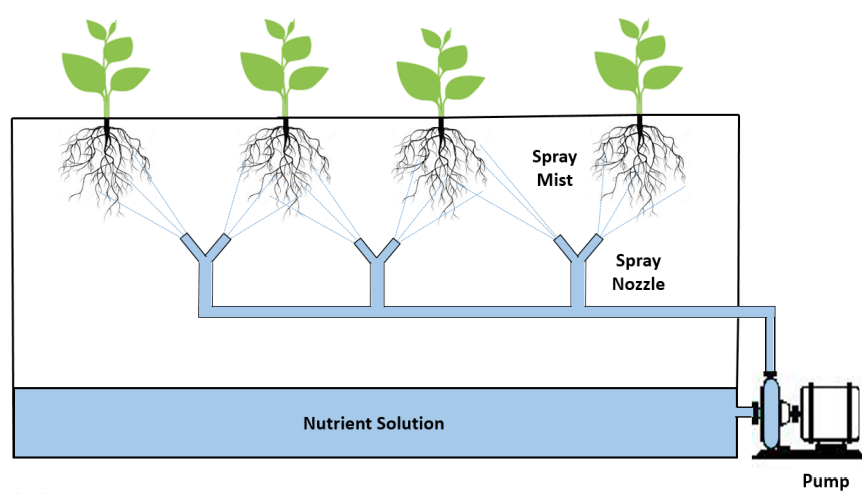
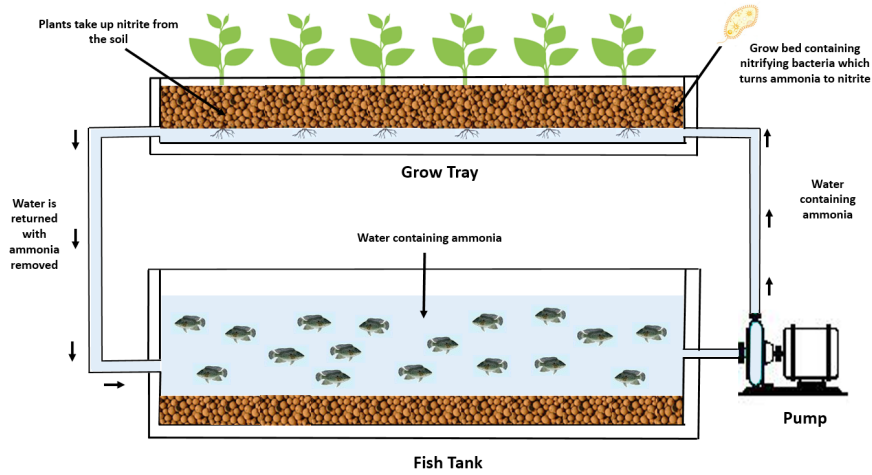
3.Aquaponics
It combines hydroponics and aquaculture, or fish farming in ponds or tanks, in a single environment. Fish raised in aquariums produce waste that is high in nutrients and can be used as a fertilizer supplement to aid in the development of plants in grow trays. On the other hand, the plants serve as a natural filter for the water in which the fish live. The grow tray is constantly supplied with ammonia-rich water from the fish tank.
Conclusion
Vertical farming technologies are still in their infancy. Companies have yet to successfully scale up crop production and make it economically feasible to meet rising food demand. SenzAgro will determine how important vertical farming will be in the future to meet the challenge of rising food demand.



