ORGANIC VS INORGANIC FARMING: Which method is more effective?

You'll see signs reading "Certified Organic" in big letters as you enter any farmers' market. Despite being much more expensive than its non-organic equivalents, organic agriculture has grown to become the most popular alternative farming method globally.
Organic agriculture is a method of farming that improves the ecosystem, soil, and human health. Organic farmers rely on natural cycles, processes, and biodiversity that are adapted to local conditions rather than man made inputs like chemical fertilizers, insecticides, and herbicides. GMOs (Genetically Modified Organisms) are used in inorganic farming to boost crop productivity but are not allowed in organic farming.
The difference between organic farming and inorganic farming

The main distinction between conventional and organic farming is the use of chemicals in conventional farming to control weeds and pests and provide plant nutrition. There are also artificial fertilizers, herbicides, and insecticides. On the other hand, organic farming relies on organic principles like biodiversity and composting to create a plentiful supply of nutritious food.
Crop rotation enhances soil fertilization and keeps the soil fertile, which is why organic farmers employ natural fertilizers. Because of the usage of synthetic pesticides and soil exploitation, inorganic farming land and soil deteriorate over time.
The main difference between organic and inorganic farming is he procedures used in organic farming do not involve any animal cruelty. Inorganic farming often injects antibiotics into livestock.
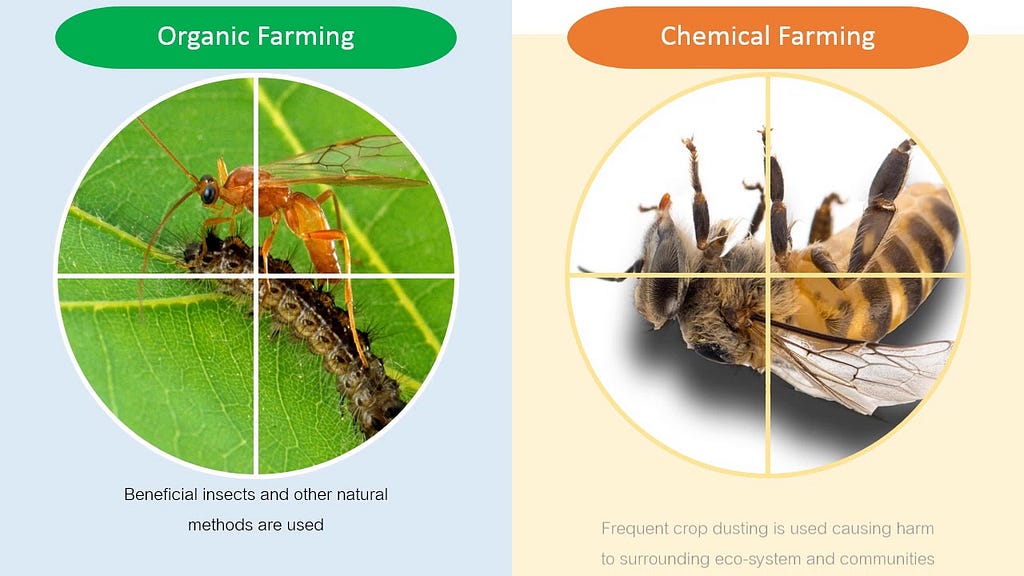
Crop rotations, the use of composted animal manures, and green manure crops are techniques that organic farmers use in ways that are economically viable in today's culture. In organic production, which emphasizes whole system health, the interaction of management techniques is the main problem. Organic farmers employ a range of methods to create and sustain biological diversity as well as to restore soil fertility.
Inorganic and organic farming practices have varying effects on the environment and people. Inorganic agriculture has an impact on increased greenhouse gas emissions, soil erosion, water pollution, and human health. In addition to avoiding dangerous pesticide residues, organic farming enhances soil health, lowers carbon emissions, and replenishes natural ecosystems for cleaner water and air.

Both organic and inorganic farming use the same techniques for harvesting, managing water resources, and preparing the land. Fertilizers used by organic farmers include paddy, husk, charcoal, gliricidia leaves, rice straw, etc. Non-organic agriculture uses fertilizers including urea, MOP, and TSP. The goal of modern or organic farming is to increase the soil's fertility, safety, and health, protect the environment, and give people access to foods that are chemical-free and high in nutrition.
You might be wondering what impact you could have in this circumstance. The farming industry is governed by the same demand-supply relationship as all other industries. If you help increase the market for goods grown organically, farmers won't have much of an option but to adapt to modern farming practices. If you must choose between the two, choose organic foods over those produced by conventional farming. Everything starts with you.




