MORE YIELD IN LESS SPACE WITH VERTICAL FARMING
The practice of growing crops in layers that are placed vertically is known as vertical farming. In order to maximize plant growth, it commonly combines soilless farming methods like hydroponics, aquaponics, and aeroponics with controlled-environment agriculture.
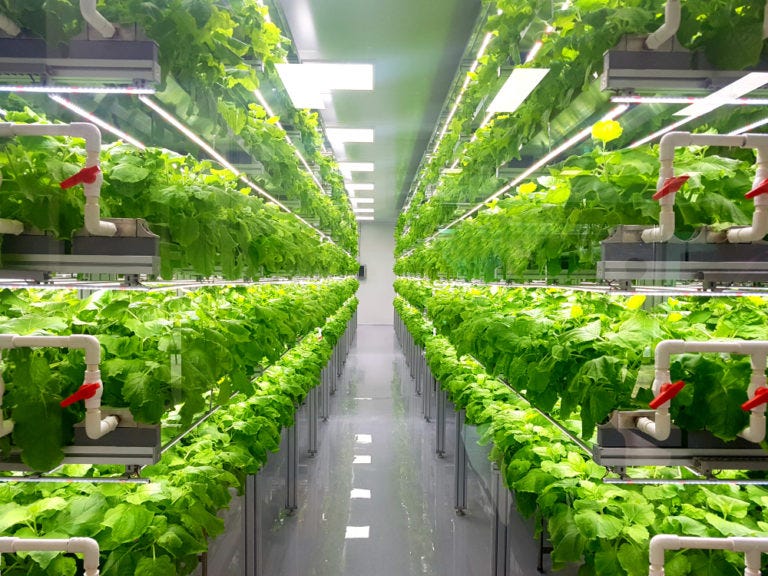

By providing access to fresh local veggies, vertical farming increases food production and expands agricultural operations. By 2050, it is predicted that two out of every three people will reside in urban areas as the global population rises.
Producing fresh vegetables close to cities helps to meet increased food demand while being environmentally responsible. While preserving essential resources like water and fertilizers, reducing the time it takes to transport fruit to cities decreases greenhouse gas emissions and boosts the availability of nutrient-dense vegetables.
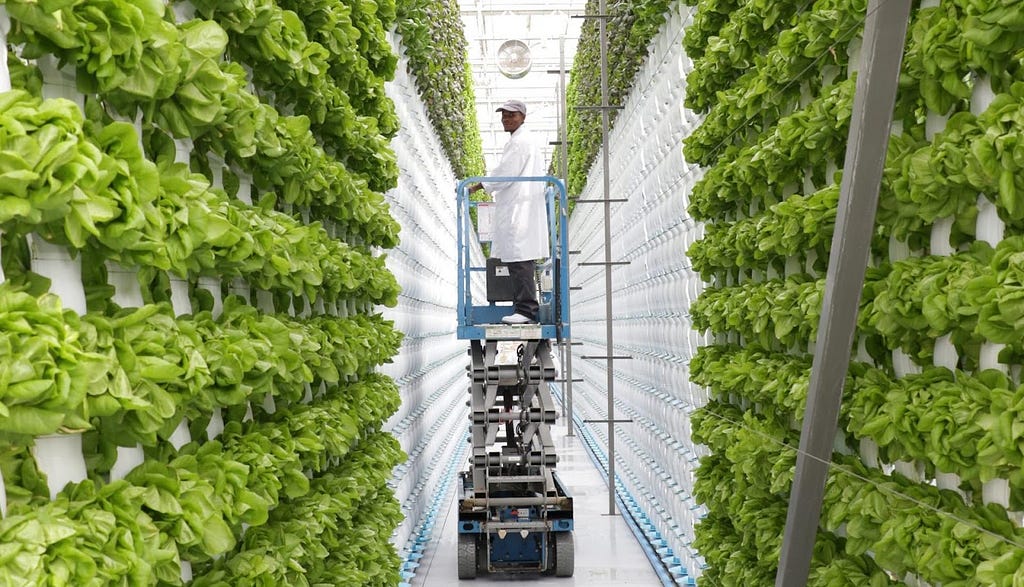

By utilizing agricultural technology, vertical vegetable garden planters can now keep an eye on any environmental conditions. You must connect vertical farming equipment to an operating system that automates processes and provides data insights if you want to make the most of it. Gaining practical knowledge makes it simpler to predict yields with more precision.
Modern vertical farming systems are gaining popularity because they can consistently produce vast amounts of high-quality crops. Growing indoors, outdoors, or in a greenhouse is a viable alternative to growing in containers.
With vertical farming, which is not weather-dependent, you may achieve a consistent crop yield throughout the year without being impacted by extreme weather conditions.
When grown in a secure, climate-controlled environment, crops can be produced with predictable results and according to a schedule. Without losing flavor or quality, automation enables quicker harvest times and greater yields.
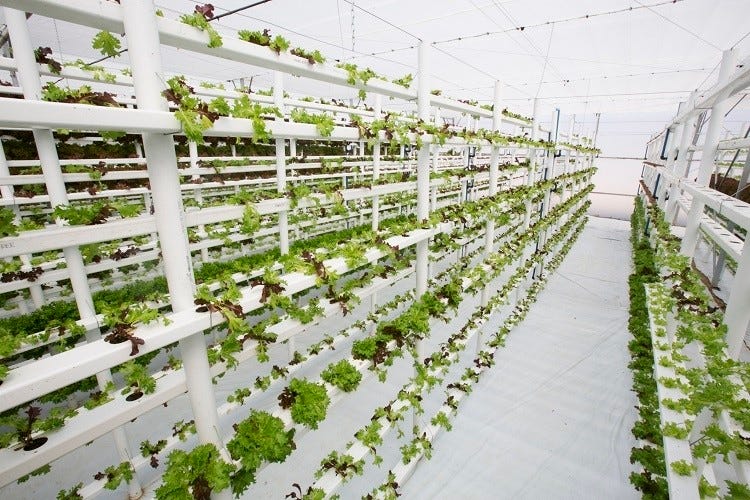

It takes a lot of fertile agricultural land to sustain traditional farms. It takes a lot of fertile agricultural land to sustain traditional farms. Regardless of climate or temperature extremes, vertical farms can be planned and built anywhere. You may accomplish more in a smaller space by developing upwards.
Depending on the crops grown, one acre of vertical farming might provide the equivalent of 10 to 20 acres of soil-based farming.
If managed properly and utilizing the required techniques, growing crops in a vertical farm can reduce the need for pesticides. A controlled environment makes it difficult for pests to propagate infestations and prevents the growth of fungi that cause diseases. Particularly when using hydroponics, vertical farms use far less water than conventional farms. Due to the fact that the water is used efficiently,
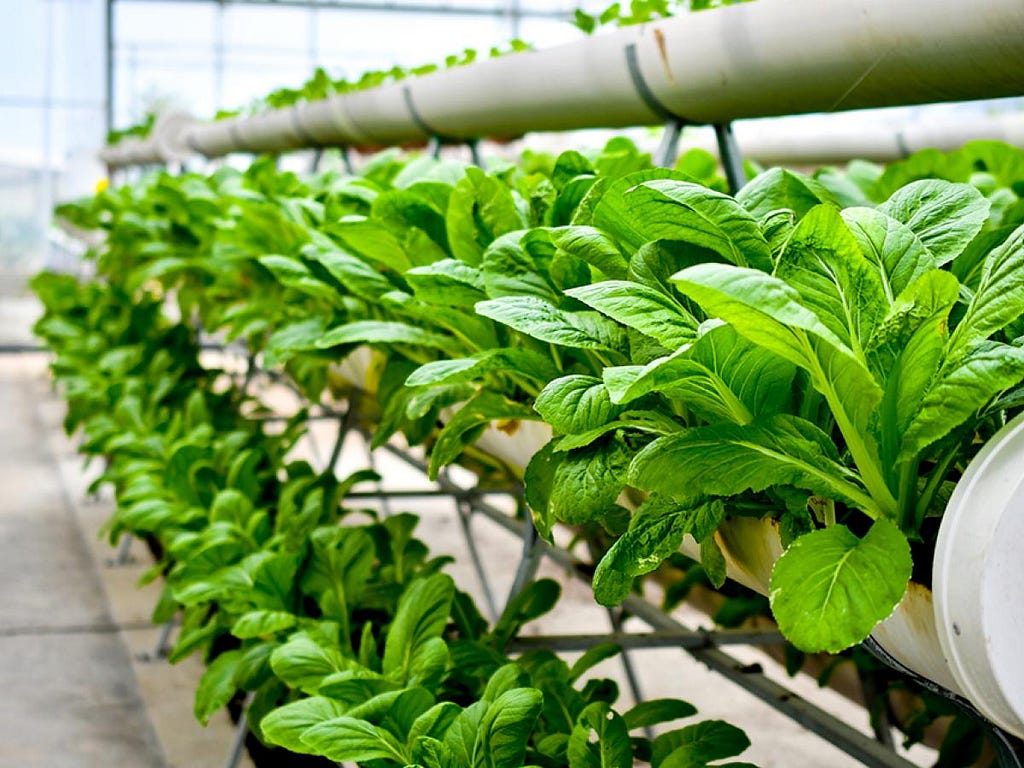

Vertical farming has many advantages, one of which is producing food closer to customers' houses. Produce is more valuable and fresher as a result of the reduction in transportation expenses, CO2 emissions, and the need for refrigerated storage.
Greenhouses and fully automated indoor growing systems don't demand a lot of physical work. The number of employees necessary to oversee the growing environment will be greatly decreased, but staff will still be needed to complete crop registration and make sure that equipment is in working order.
The UAE has been a regional pioneer in providing funding for agricultural technology (AgTech) initiatives that would improve national food security. The UAE has a chance to play a significant role in the vertical farming industry.
Without a doubt, vertical farming is converting deserts into markets for fresh food. Numerous studies have found that compared to field farms, vertical farms produce 516 times as much per 10,000 square meters on average. According to a 2017 survey on indoor farms, vertical farms generated 5.45 pounds of lettuce on average per square foot. In the meantime, only 0.69 pounds of lettuce were grown by field farms in the meantime.
Together, these solutions automate most of the previously time-consuming operations. You may learn a lot about your indoor vertical farm if it is connected, including how to water, fertilize, heat, cool, and open curtains or vents.




