YOUR KEY TO SUCCESS: GREEN HOUSE FARMING!
Due to the crops' frequent exposure to bad weather, crop cultivation is a challenging task. The pace of agricultural production is significantly influenced by weather and climate conditions. However, limitations have no place when agricultural production plays a significant role. Hence, techniques that involve farming in a controlled environment were developed as a result of the search for solutions.
One of the fundamental types of farming within a controlled environment is greenhouse farming.

What is Greenhouse farming?
Greenhouses have been used for centuries to cultivate plants and flowers, and the history of greenhouse farming can be traced back to ancient Roman times. In Europe, greenhouses began to be used more extensively in the 16th century, when the Dutch and the English began to use them to grow exotic plants and flowers for export. The first large-scale commercial greenhouses were built in the Netherlands in the early 19th century, and the use of greenhouses for commercial food production became more widespread in the 20th century.
Nowadays, greenhouses are used all over the world for a variety of purposes - be it for food production, plant research, or even floriculture.. They can be used to nurture plants in environments where it may not be possible to grow them, such as in cold climates or in urban areas of limited space.
Greenhouse farming is a type of agriculture in which plants are grown in a controlled environment, typically in a greenhouse. A greenhouse is a structure made of glass or plastic that allows sunlight to pass through and warms the air inside, creating a warm and humid environment suitable for plant growth. Greenhouses can be used to grow a wide variety of plants, including vegetables, fruits, flowers, and herbs.
Importance of greenhouse farming
A greenhouse allows you to concoct the most divine combinations for your garden, experiment with your ingredients, and nurture the most wonderful flora, fauna and other vegetation. It provides a nurturing, caring environment with just the right conditions for optimal plant growth.
Like all great food production, even plants need the finest ingredients; quality ingredients that a greenhouse enhances.
First, they need light as the energy source for photosynthesis - which can be easily achieved via a greenhouse who harnesses the power of the sun through its glass panels. Without light your plants cannot grow. It’s as simple as that. A greenhouse helps amplify light inputs and also provide a protected place for your plants to grow.
Plants need water and carbon dioxide. The water molecules in the reaction are broken down and release oxygen into the atmosphere. Plants take in carbon dioxide and produce carbon chains in the form of sugars and plant foods. This is then used to fuel growth and store the carbon chains within the structure of their leaves and fibers, transforming them into virtual carbon sinks - which is exactly why planting trees and growing plants is good for the planet. As long as there is good ventilation and airflow inside your greenhouse, there will be plenty of carbon dioxide.
Bear in mind that in the absence of light (such as at night or intense shade) your plants will respire and produce carbon dioxide, enriching the greenhouse’s air with CO2.This, in turn, is used during the day for the plants to photosynthesize. At the end of the process, you find its waste product (which is our lifeline– OXYGEN. This is why trees and plants are regarded as the lungs of our planet. In a nutshell the greenhouse provides, enhances and supports the perfect conditions for photosynthesis; the method in which plants make food and grow.
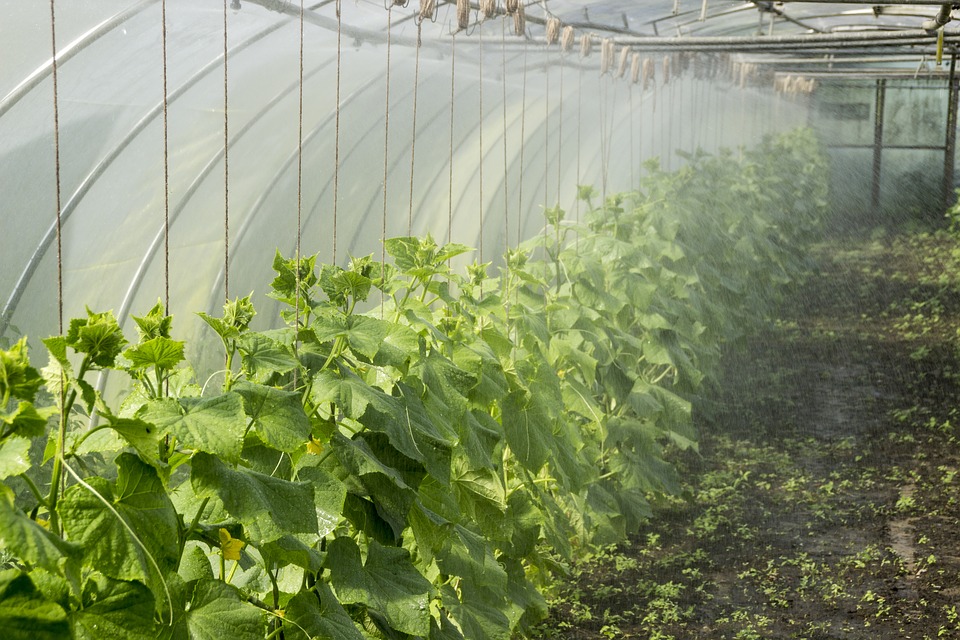

Benefits and Challenges in greenhouse farming
Benefits
- Increased crop production
Greenhouse farming allows farmers to grow crops year-round, regardless of the weather conditions outside. This can help increase food production and improve food security, especially in areas with extreme temperatures or limited sunlight.
- Increased crop production
- Reduced water usage
Various irrigation systems (such as drip, sprinklers, and more) can be automated, customized, and used in a greenhouse, which end up being more efficient in delivering water to plants - hence reducing overall water usage.
- Reduced pest and disease pressure
- Improved sustainability
- Increased economic opportunities
- Improved food safety
The controlled environment of a greenhouse allows farmers to carefully regulate temperature, light, moisture, and nutrient levels, leading to higher-quality and more consistent crops.
The controlled environment of a greenhouse can help reduce the risk of pests and diseases, as the greenhouse can be designed to exclude these factors.
Greenhouse farming can help reduce the impact of climate change on agriculture by allowing farmers to grow crops in a more controlled and sustainable manner.
Greenhouse farming can provide great economic opportunities for farmers - especially in areas with limited natural resources or adverse growing conditions.
The controlled environment of a greenhouse can help reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses by minimizing the risk of contamination from pests, diseases, and other external factors.
Challenges
- High operating and Up-front cost
- Pest without pollination and pesky pests
if you want to make the most of your greenhouse, you should spend money on a kit or materials that have a long lifespan and the right qualities for the plants you wishto cultivate.. A relatively high operating cost may be associated with maximum climate control. Additionally, your monthly expenses will significantly increase if you decide to heat your greenhouse using gas or electric heaters.
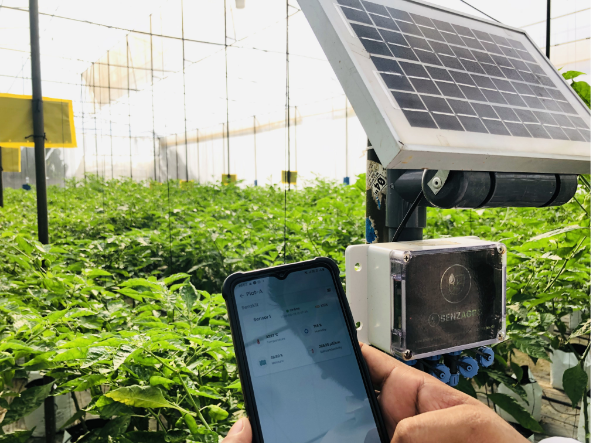
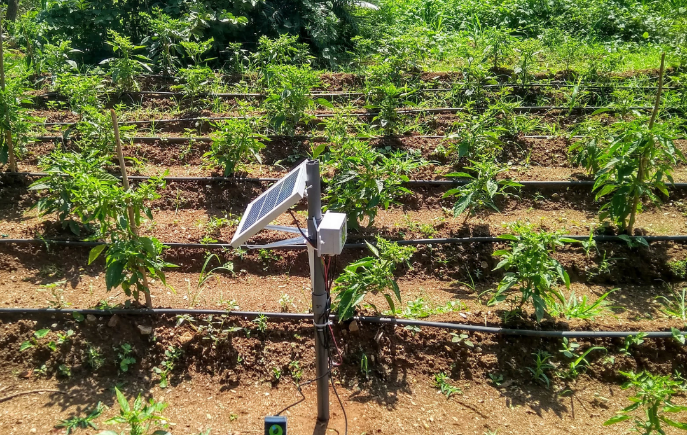
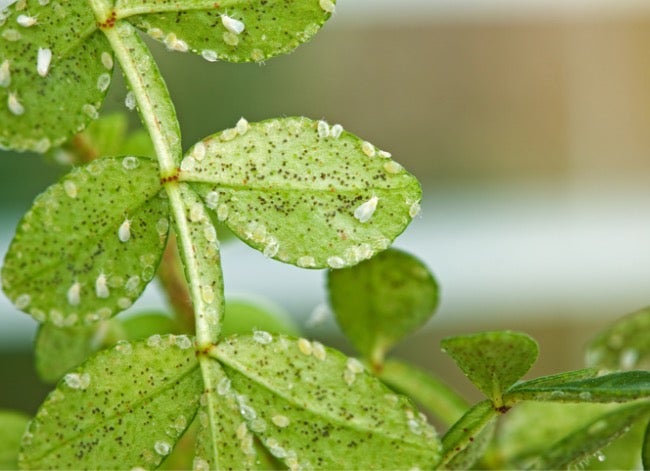
The majority of what your plants come into touch with can be controlled by having a greenhouse, but if one or two of your plants have pests like whiteflies or diseases, they can quickly spread to the rest of your plants, hence ruining your entire crop. To ensure that your next crop won't be impacted, careful measures must be made to eradicate any pests or diseases. See how SenzAgro helped counter this issue via thier pest controlling system and smart farming techniques:

- Management of Temperature and Ventilation
A greenhouse, which is intended to keep heat inside during the cold months, also acts as a heat trap in the summer. Plants can be roasted to death if temperatures are too high. If temperatures fall too far during the colder months, plants will freeze to death.
How does the greenhouse system work?
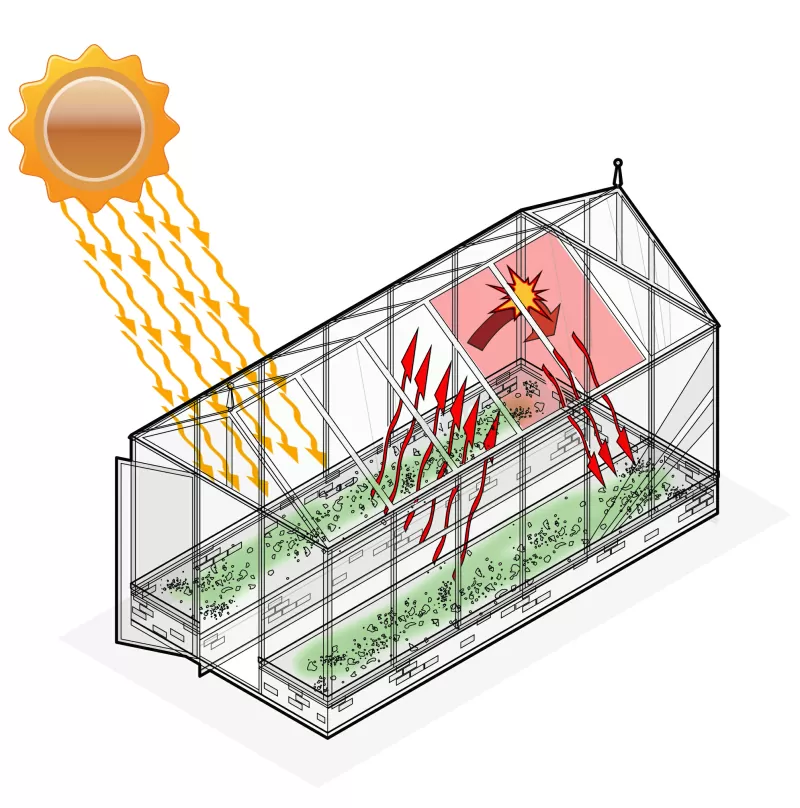
The "greenhouse effect" is a fundamental physical concept that underlies every greenhouse's operation. Short wavelengths of sunlight can travel through translucent or transparent materials like glass or plastic. Some of the light energy is converted into heat when it strikes an obscure surface indoors, such as plant leaves, greenhouse floors, or planters.
More heat is produced on surfaces that are darker, as darker shades tend to absorb more light. Light (but not heat) can be effectively transmitted through the greenhouse panels. Thus, the majority of the heat is trapped inside.
Short waves warm the ground once they arrive. The greenhouse is then heated as the warm air rises. The atmosphere is reached by the long waves.
Greenhouses can be used to grow plants during the winter months, even in areas with cold temperatures and short days. The insulation provided by the greenhouse structure and the trapping of solar radiation inside the space help to keep the air and soil warm, allowing plants to continue growing.
However, it's important to maintain the greenhouse environment properly during the winter to ensure that the plants receive the necessary heat, light, and water. This may involve using supplementary lighting or heating, adjusting the ventilation, and monitoring the temperature and humidity inside the greenhouse.
It's generally best to locate a greenhouse in a sunny location, as this will allow the maximum input of sunlight that is essential for plant growth. However, it's important to consider the specific needs of the plants that will be grown in the greenhouse, as some plants may require partial shade or may be sensitive to excessive heat or light.
Types of greenhouse farming
There are several types of greenhouse farming, each with its own unique characteristics and benefits. Here are a few common types of greenhouse farming:
- Traditional greenhouse
- Hydroponic greenhouse
- Aquaponic greenhouse
- Passive solar greenhouse
- Vertical greenhouse
A traditional greenhouse is a standalone structure made of glass or plastic that is used for growing plants. These greenhouses are often used to extend the growing season and to grow a wide variety of plants, including vegetables, herbs, and flowers.

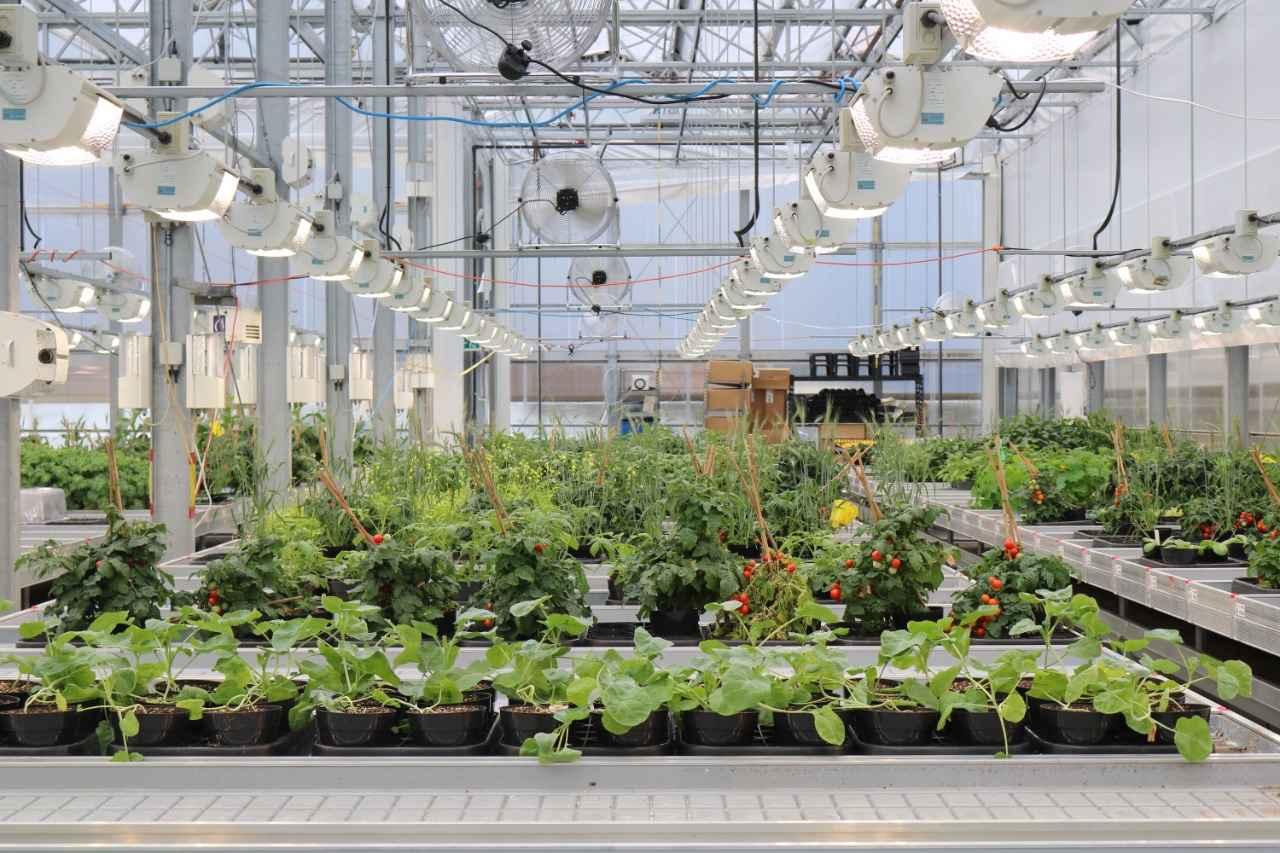
A hydroponic greenhouse is a specialized greenhouse that uses nutrient-rich water instead of soil to grow plants. This type of greenhouse is highly efficient and can be used to grow a wide range of crops, including vegetables, herbs, and flowers.

An aquaponic greenhouse combines hydroponics with aquaculture (the cultivation of fish or other aquatic animals) to create a symbiotic system in which the waste produced by the fish is used to fertilize the plants, while the plants help to filter the water for the fish.

A passive solar greenhouse is designed to make use of the sun's energy to heat the greenhouse and keep it warm without the need for additional heating systems. These greenhouses are often constructed using insulated materials and are designed to capture and retain solar heat.
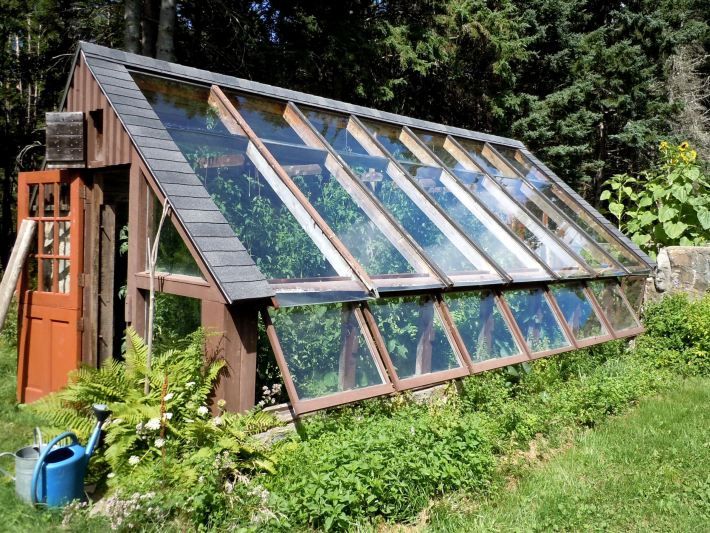

A vertical greenhouse is a specialized greenhouse that is designed to grow plants in a vertical rather than horizontal orientation. These greenhouses are often used to maximize space and can be used to grow a wide range of crops, including vegetables, herbs, and flowers.

Future of greenhouse farming
In the future, greenhouse farming is likely to continue to be an important part of the agriculture industry, allowing the production of high-quality crops in a controlled environment that can be managed to optimize its growth and productivity. This can be particularly beneficial in areas with challenging weather conditions or soil quality, as greenhouses allow for the creation of a more favorable growing environment.
One trend that is likely to continue in the future of greenhouse farming is “A greenhouse monitoring system” used to monitor and control the growing conditions in a greenhouse in the absence of people. This may include the use of sensors to monitor temperature, humidity, and other factors, as well as the use of hydroponic systems to deliver water and nutrients directly to the plants. In addition, there is likely to be a continued focus on sustainability in greenhouse farming, including the use of renewable energy sources and the measures taken to minimize the overall impact on the environment.
The future of greenhouse farming looks bright, as it provides a way to produce high-quality crops in a controlled and sustainable manner, however always bear in mind that the correct equipment, supplies, and technologies are used
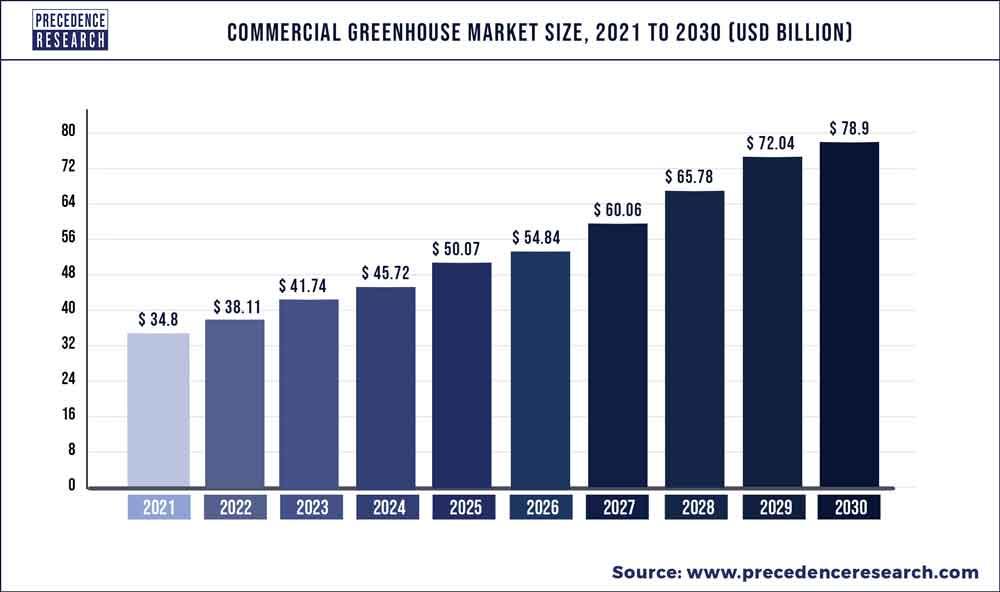
According to precedence research the global commercial greenhouse market size accounted for USD 34.8 billion in 2021 and is expected to hit around USD 78.9 billion by 2030, poised to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.52% from 2022 to 2030
For instance, Village Farms, based in Delta, British Columbia, Canada, is a leading producer of greenhouse-grown vegetables, including tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers. The company operates over 6 million square feet of greenhouse space in Canada and the United States.
Conclusion
Greenhouse farming is a growing industry that has the potential to increase crop yields, improve food security, and reduce the environmental impact of agriculture. By nurturing crops in a controlled environment, greenhouse farmers can manipulate and optimize growing conditions to produce high-quality crops all year-round. Furthermore, involving the use of technology and sustainable practices in greenhouse farming can help increase efficiency and reduce resource usage,thereby reducing the overall impact on the environment
For more info please visit here




